Pseudo-classes
In CSS, a pseudo-class is used to define the special state of an element.
For example:
- Change the style when a user hovers over a link.
- Style visited links differently.
- Highlight the first child of a parent element.
Syntax
selector:pseudo-class {
property: value;
}
Here, pseudo-class is applied to the selector when it is in a particular state.
Pseudo-classes for Links
Links are commonly styled using pseudo-classes.
1. :link
Applies to links (<a>) that have not been visited yet.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Link Example</title>
<style>
a:link {
color: blue;
text-decoration: none;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>:link Example</h2>
<a href="https://www.example.com">Go to Example.com</a>
</body>
</html>
Output

The link appears blue and without underline if it hasn’t been clicked before.
2. :visited
Applies to links that the user has already clicked.
a:visited {
color: purple;
}
Effect: After visiting the link, it will turn purple.
3. :hover
Triggers when the user moves the mouse pointer over an element.
a:hover {
color: red;
text-decoration: underline;
}
Effect: When hovering over the link, it becomes red and underlined.
4. :active
Applies to a link when it is being clicked.
a:active {
color: orange;
}
Effect: While pressing the link, it briefly appears orange.
Full Example with All Link Pseudo-classes
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Link Pseudo-classes</title>
<style>
a:link {
color: blue;
}
a:visited {
color: purple;
}
a:hover {
color: red;
}
a:active {
color: orange;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>CSS Link Pseudo-classes</h2>
<a href="https://www.example.com">Visit Example.com</a>
</body>
</html>
Output:
- Normal: Blue
- After click: Purple
- On hover: Red
- While clicking: Orange
Structural Pseudo-classes
Besides links, there are pseudo-classes for targeting elements based on their position in the DOM.
1. :first-child
Selects the first child of a parent.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>First Child Example</title>
<style>
p:first-child {
color: green;
font-weight: bold;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<p>I am the first paragraph inside div.</p>
<p>I am the second paragraph.</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>
Output:
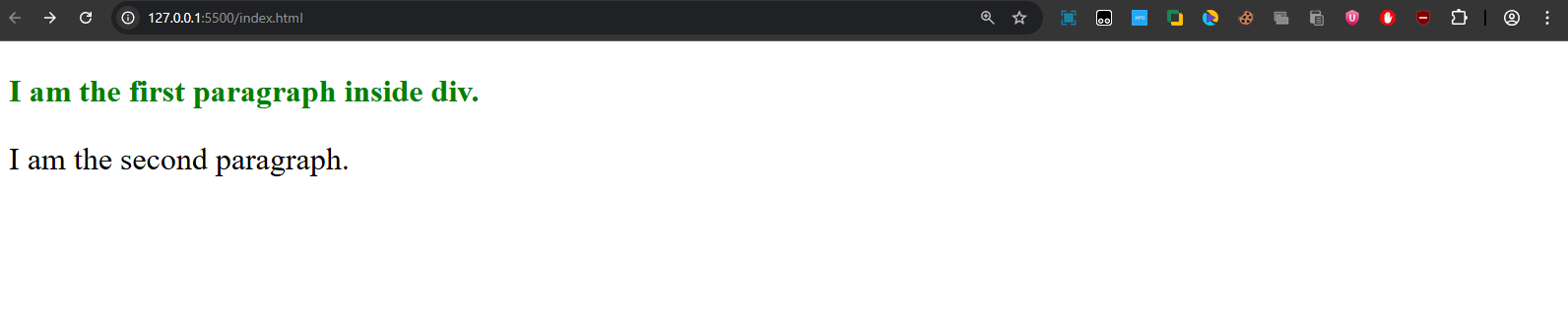
The first paragraph inside the div is styled green and bold.
2. :last-child
Selects the last child of a parent.
p:last-child {
color: blue;
}
Effect: Only the last paragraph inside its parent becomes blue.
3. :nth-child(n)
Selects elements based on their position (n = number or formula).
li:nth-child(2) {
color: red;
}
Effect: The second list item becomes red.
You can also use formulas like nth-child(odd) or nth-child(2n) for patterns.
4. :not(selector)
Selects all elements except the ones matching the selector.
p:not(.highlight) {
color: gray;
}
Effect: All paragraphs except those with class highlight are gray.
Quick Recap -
- Link pseudo-classes: :link, :visited, :hover, :active.
- Structural pseudo-classes: :first-child, :last-child, :nth-child(), :not().
- Pseudo-classes let you style elements based on state or position without adding extra classes in HTML.