Pagination
Pagination is a way of splitting content into separate pages and providing navigation links (like 1, 2, 3 ... Next) to move between them. While CSS doesn’t have a direct pagination property, we can style HTML links to create a professional-looking pagination bar.
Example:
Pagination is built with a simple list of anchor (<a>) links.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>CSS Pagination Example</title>
<style>
/* Container */
.pagination {
display: inline-block;
margin: 20px 0;
}
/* Pagination links */
.pagination a {
color: black;
float: left;
padding: 10px 16px;
text-decoration: none;
transition: background-color 0.3s;
border: 1px solid #ddd;
margin: 0 4px;
font-size: 18px;
}
/* Active page */
.pagination a.active {
background-color: #6c5ce7;
color: white;
border: 1px solid #6c5ce7;
}
/* Hover effect (not on active) */
.pagination a:hover:not(.active) {
background-color: #333;
color: white;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>CSS Pagination Example</h2>
<p>Hover and click through the page numbers below:</p>
<div class="pagination">
<a href="#">«</a>
<!-- Previous -->
<a href="#">1</a>
<a href="#" class="active">2</a>
<a href="#">3</a>
<a href="#">4</a>
<a href="#">5</a>
<a href="#">6</a>
<a href="#">»</a>
<!-- Next -->
</div>
</body>
</html>
Output:
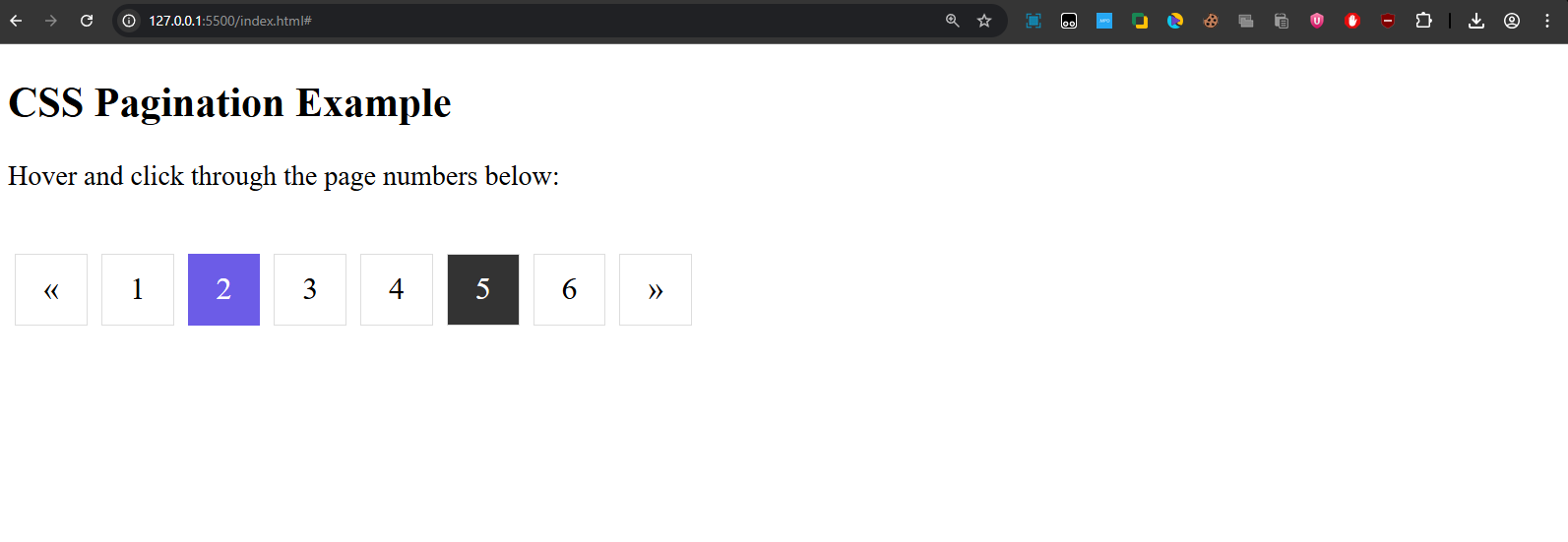
- Page numbers are styled as buttons.
- The current page (2) is highlighted in purple.
- On hover, other links turn black with white text.
- Smooth transition effect enhances user experience.
Pagination isn’t an inbuilt CSS property but can be created easily using HTML links styled with CSS. It improves navigation, readability, and user experience on websites with multiple pages.