Border Images
Borders in CSS aren’t limited to just solid, dashed, or dotted lines. With the border-image property, you can use custom images as borders around elements. This allows you to create creative, decorative frames and unique styling for text, divs, or boxes.
For example: Let’s try adding this image as a background around the text.
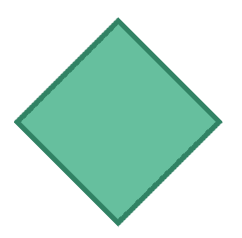
Syntax of border-image:
selector {
border: width style color; /* Must declare a border */
border-image-source: url(image.png); /* The image to use */
border-image-slice: value; /* How the image is divided */
border-image-repeat: stretch | repeat | round; /* How it’s repeated */
}
The border property (width + style) is mandatory because border-image replaces the border style.
Example 1: Basic Border Image
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>CSS Border Image - Basic Example</title>
<style>
body {
font-family: Arial, sans-serif;
background: #f7f7f7;
padding: 30px;
text-align: center;
}
.box {
width: 300px;
margin: auto;
padding: 20px;
font-size: 18px;
border: 20px solid transparent; /* border width is required */
border-image: url('https://cwh-full-next-space.fra1.digitaloceanspaces.com/tutorial/css-border-images/border.webp') 30 round;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>Basic Border Image</h2>
<div class="box">This box uses an image as its border.</div>
</body>
</html>
Output:
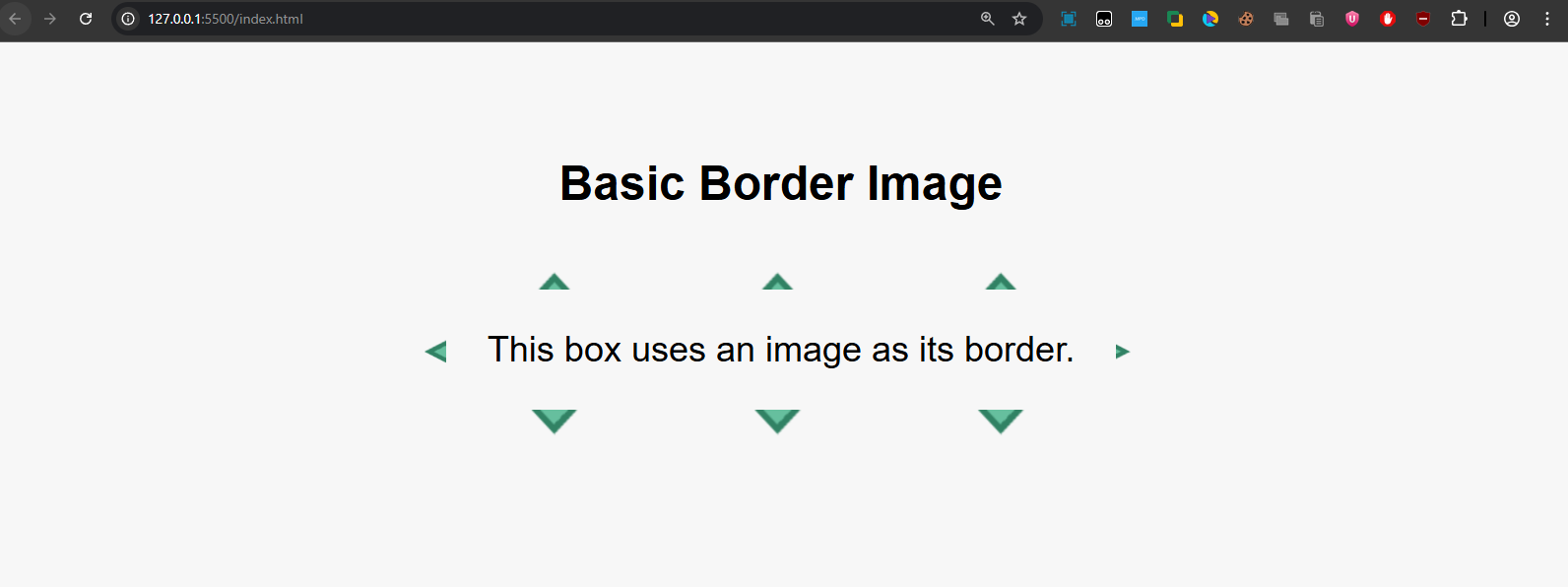
- The border-image property replaces the normal border with the image.
- The 30 is the slice value (cutting parts of the image).
- The round keyword ensures the border image tiles evenly around all sides.
Example 2: Changing Border Slice Values
The border-image-slice defines how much of the image is used for the border.
- Smaller values = thinner border pieces.
- Larger values = thicker border pieces.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>CSS Border Image - Slice Example</title>
<style>
body {
font-family: Arial, sans-serif;
background: #f7f7f7;
padding: 30px;
text-align: center;
}
.box {
width: 280px;
margin: 20px auto;
padding: 20px;
border: 20px solid transparent;
border-image-source: url('https://cwh-full-next-space.fra1.digitaloceanspaces.com/tutorial/css-border-images/border.webp');
border-image-repeat: round;
}
.slice30 {
border-image-slice: 30;
}
.slice50 {
border-image-slice: 50;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>Border Slice Values</h2>
<div class="box slice30">This uses <b>30%</b> slice</div>
<div class="box slice50">This uses <b>50%</b> slice</div>
</body>
</html>
Output:
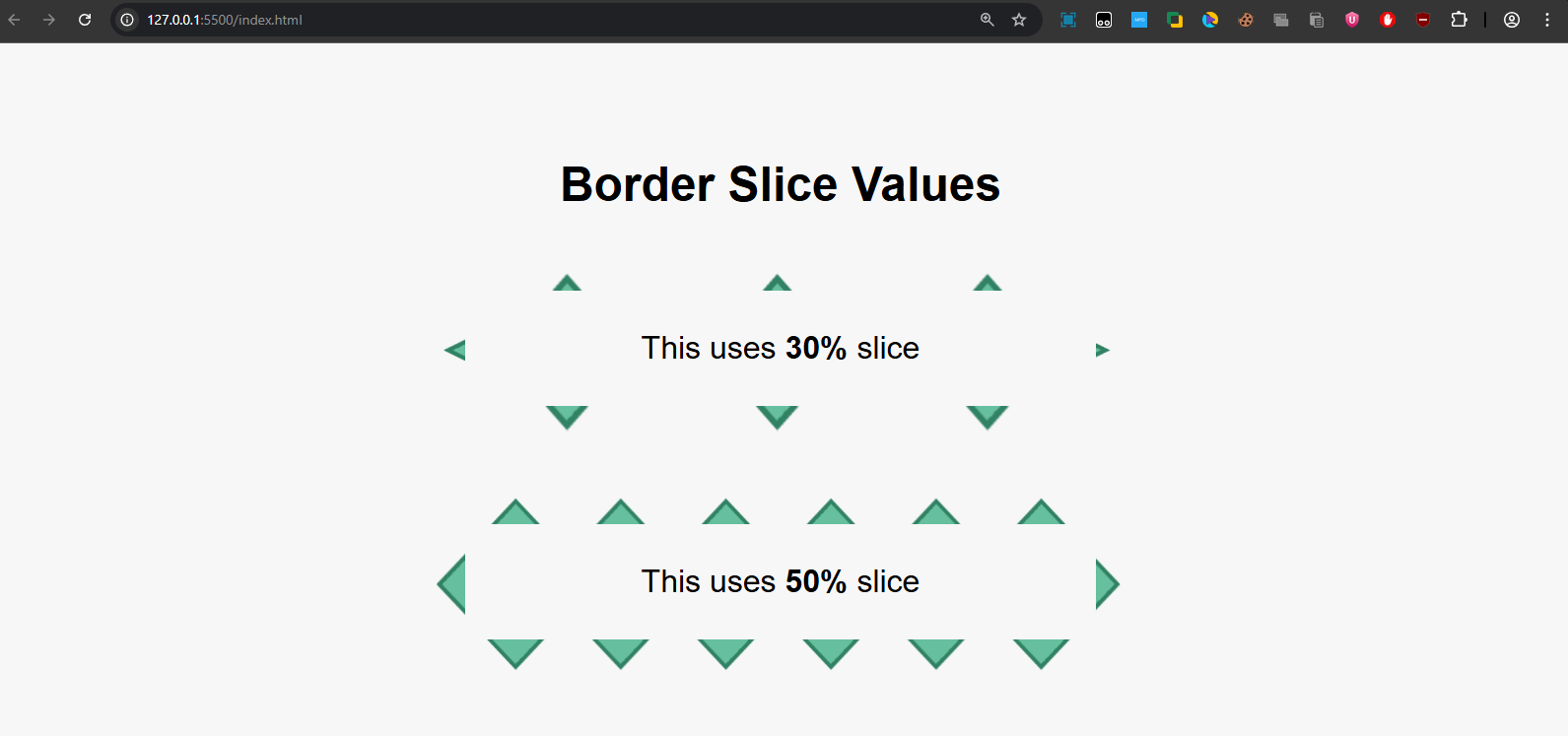
- The first box (30%) shows a tighter, smaller border image.
- The second box (50%) makes the border image appear thicker and bolder.
Key Points to Remember
- Always declare border: X solid transparent; before using border-image.
- Use border-image-slice to control how much of the image is used.
- border-image-repeat helps decide whether the image should stretch, repeat, or round.
- This property works best with symmetric decorative images like frames or patterns.