Overflow
Sometimes, content inside an element is larger than the available space. If not handled properly, this can break the layout or hide important information.
CSS provides the overflow property to control how excess content is displayed.
Syntax
selector {
overflow: value;
}
Values can be:
- visible
- hidden
- scroll
- auto
Overflow Visible
This is the default behavior. The content will simply spill out of the container, even if it overflows.
Example:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>CSS Overflow</title>
<style>
div {
background-color: rebeccapurple;
width: 200px;
height: 80px;
overflow: visible;
border: 2px solid;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet consectetur adipisicing elit. Voluptates impedit error quisquam unde libero incidunt id nobis, commodi, impedit est iure ansa fugit facilis necessitatibus? Architecto cum est tempore voluptas!
Fugiat fugit. Repudiandae inventore eaque expedita consectetur dolore deleniti nostrum vero odit distinctio temporibus, dolus vel explicabo ut ea itaque quibusdam laborum?
</div>
</body>
</html>
Output:

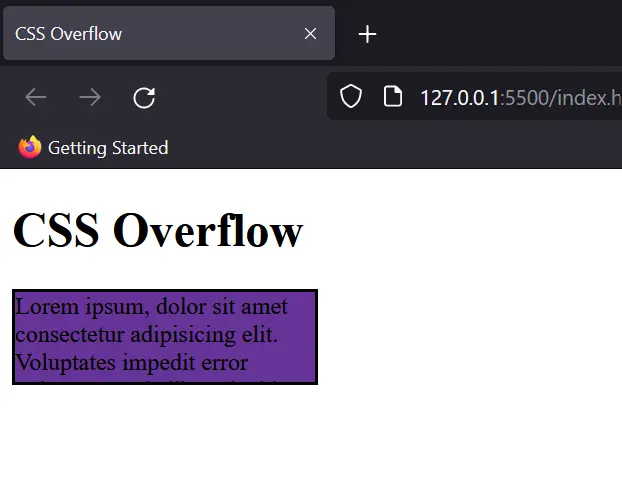
Overflow Hidden
When hidden is used, any extra content that does not fit inside the container will be cut off.
Example:
div {
background-color: rebeccapurple;
width: 200px;
height: 60px;
border: 2px solid;
overflow: hidden;
}Output:
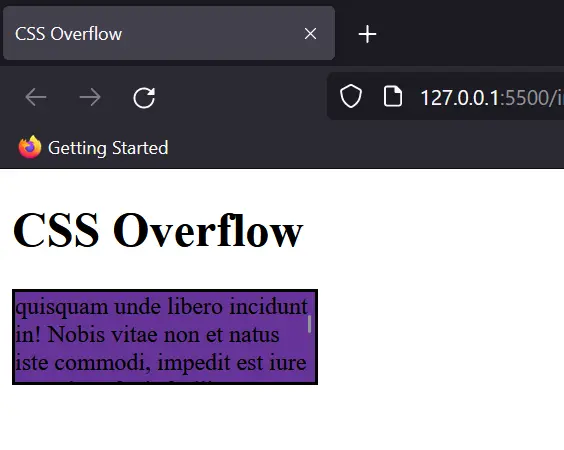
Overflow Scroll
With scroll, the container always shows scrollbars, regardless of whether the content overflows or not.
Example:
div {
background-color: rebeccapurple;
width: 200px;
height: 60px;
border: 2px solid;
overflow: scroll;
}Output:
Overflow Auto
It is quite similar to scroll but the scroller is only added when the content starts getting out of the container. Mostly this option is used to avoid unnecessary scroll bars if the content already is within the content dimensions.
Quick Recap
- visible → Content spills outside (default).
- hidden → Extra content is cut off.
- scroll → Always adds scrollbars.
- auto → Adds scrollbars only when needed (recommended).